Projects
T2M-X: Learning Expressive Text-to-Motion Generation from Partially Annotated Data [paper][appendix][demo]
2023 Intern at Sanp Research
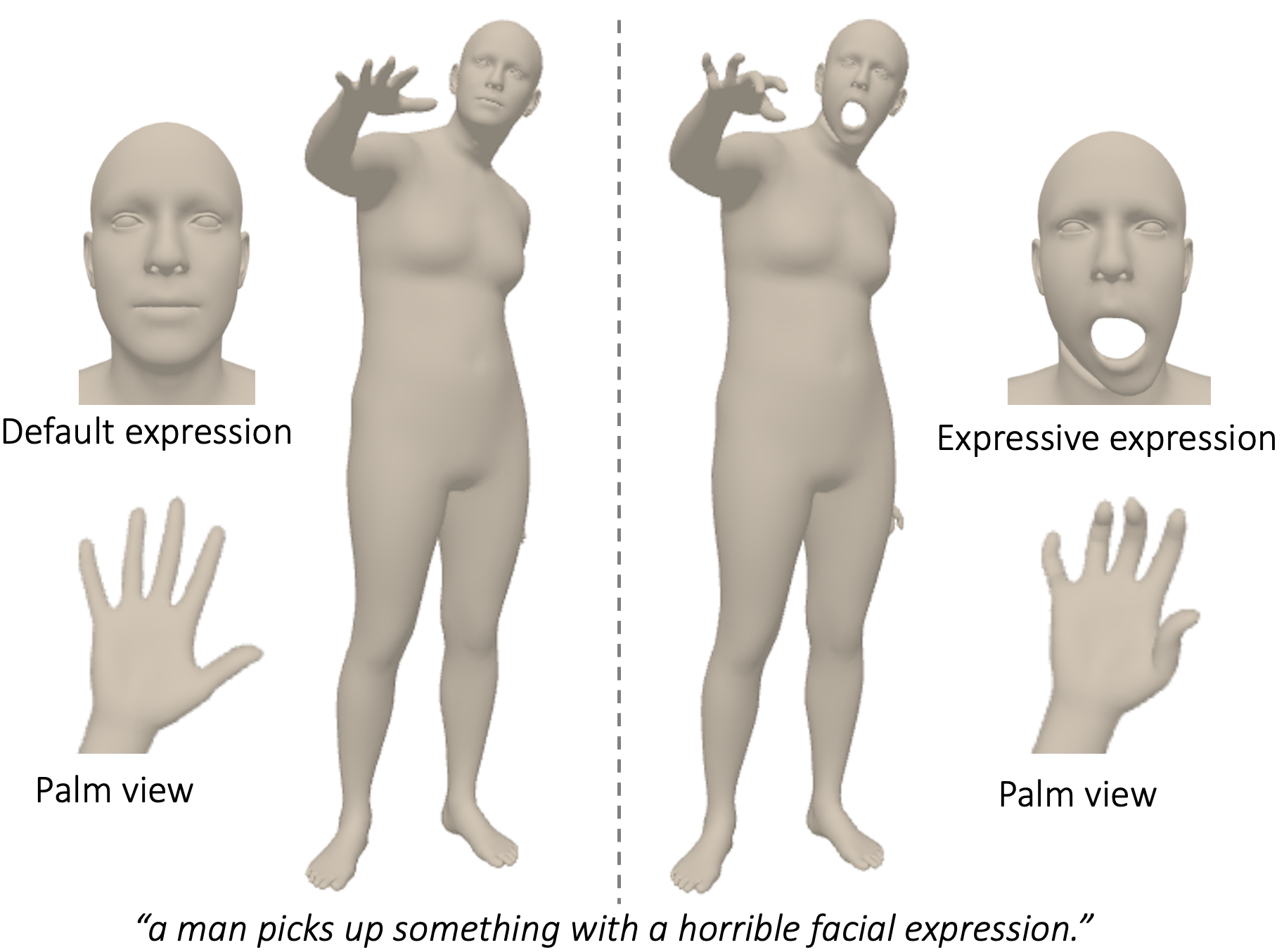
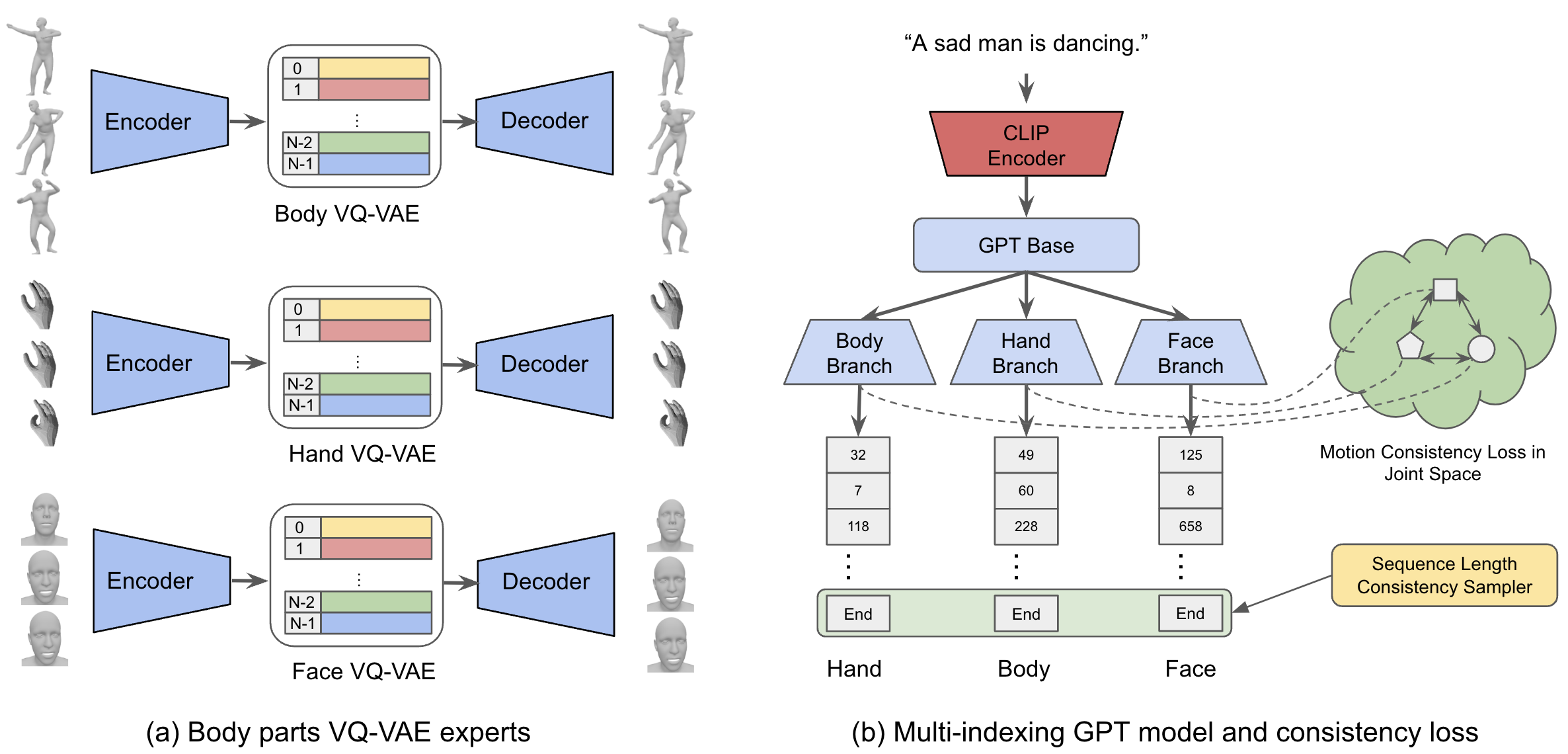
The generation of humanoid animation from text prompts can have profound impact on animation production and AR/VR experiences. However, existing methods only generate body motion data, excluding facial expressions and hand movements. This limitation, primarily due to a lack of comprehensive whole-body motion dataset, inhibits their readiness for production use. Recent attempts to create such a dataset have resulted in either motion inconsistency among different body parts in the artificially augmented data or lower quality in the data extracted from RGB videos. In this work, we propose T2M-X, a two-stage method that learns expressive text-to-motion generation from partially annotated data. T2M-X trains three separate Vector Quantized Variational AutoEncoders (VQ-VAEs) for body, hand and face on respective high quality data sources to ensure high quality motion outputs, and a Multi-indexing Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) model with motion consistency loss for motion generation and coordination among different body parts. Our results show significant improvements over the baselines both quantitatively and qualitatively, demonstrating its robustness against the dataset limitations.
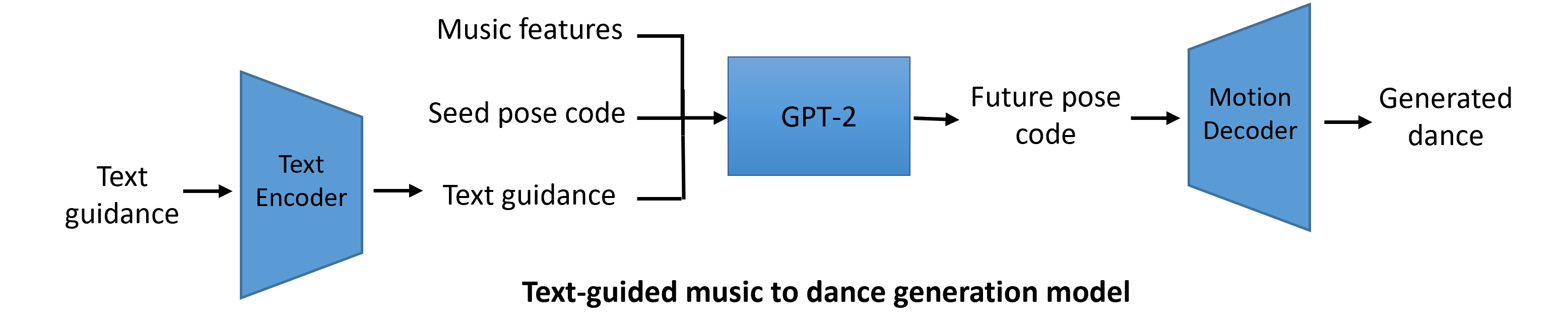
Text-guided music to dance generation [demo][slides]
2022 Summer Intern at Alexa AI
Generating 3D dances from music is an emerging research topic that can enable delightful use cases such as dance trainer, dance animator for avatars, etc. The generated dance motion should conform to constraints of human body mechanics such as not hyperextend elbows, and have realistic movements that a human could perform. Previous works approaches use techniques such as Full-Attention Transformer, add physics-based constraints and leverage VQ-VAE for feature extraction and fusion to generate diverse dance movements. However, these methods do not generalize well to new music. Further, these dance motions cannot be easily edited by customers by saying simple text commands such as “Move your right arm up”. We propose an alternative approach where we project dance movements and corresponding text descriptions of motion to a common latent space. A dance motion codebook conditioned on music features (genre, audio spectogram, beats per minute) is used to predict these latent space variables, thus allowing us to generate realistic dance motions and empower our customers to edit dance movements by using simple text/voice commands. Our model produces realistic dance predictions. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method can enable both algorithmic and personalized dance motion generation from music.


Smart watch-based hand gesture reognition model for AR glasses [demo][patent][media1][media2][media3]
2021 Summer Intern at OPPO US Research Center
Augumented reality (AR) glasses are the promising commerical products as the enterance to Metaverse. However, the common user interface (UI) for AR glass is the vision-based hand gesture recognition which can only capture the gestures in the view of camera. This limit the usage of AR glass. Here, we proposed a smart watch-based hand gesture recognition system which takes the data from Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor and Photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor as input and predicts user’s hand gesture in real time. A modified MobileNet deep learning model was trained on 0.4 million data collected from various users. The well-trained model has averaged 96% recall and 94% precision for each type of gesture. By combining handcrafted signal features into the model, we reduced 35% power consumption over existing methods. You can check the demo here.

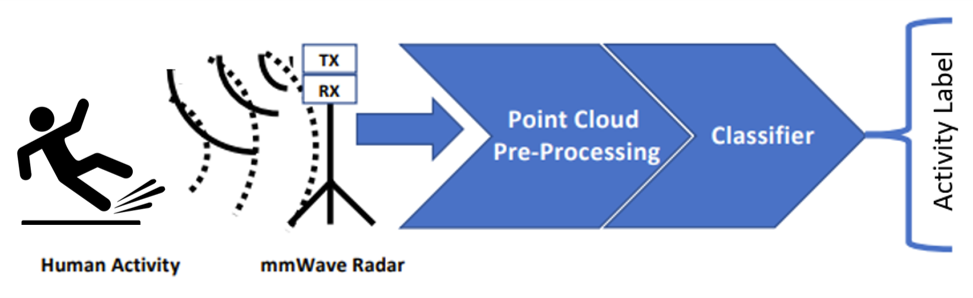
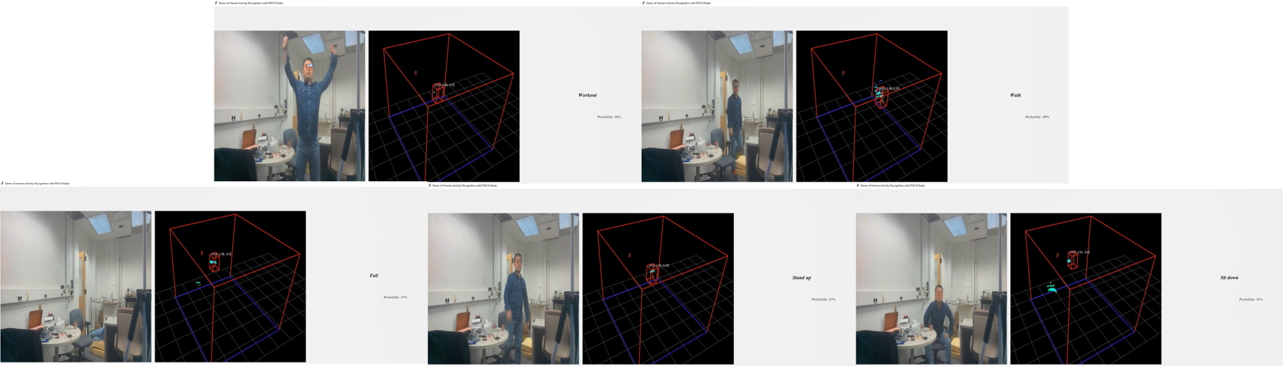
Indoor Activity Recognition with mmWave Radar Sensor for Aging in Place [project homepage] [demo] [presentation] [code]
Computer Science master thesis
Nowadays, world population aging, which requires heavy investment of time and manpower in daily care, is having a heavy impact on society and economic of human beings. To caregivers, injury or death caused by fall-down and declined self-dependence due to Alzheimer’s disease are two main issues to struggle on. Herein, we devise a human activity recognition (HAR) system which is potential to handle these issues. In contrast to traditional system using RGB camera, the indoor activity recognition system with mmWave Radar offers an service with low privacy leakage risk without costing any recognition accuracy. Taking the data of daily indoor activities as input, four deep learning models are trained and com- pared to build up an optimized activity classifier. The averaged accuracy of best model in test data set reaches 91.87%, which shows its full potential for practi- cal deployment. A simplistic user interface (UI) is also designed to demonstrate the functionality of well-trained model. To implement distributed deployment, we connect Raspberry Pi to AWS IoT for real-time data collection and processing respectively. A probability threshold of fall-down action is set by AWS Lambda to trigger an alarming and call for first-aid in time. We hope the proposed system could provide an accurate recognition service which further enable the remote monitoring for elderly people and reduce labour for caregivers.
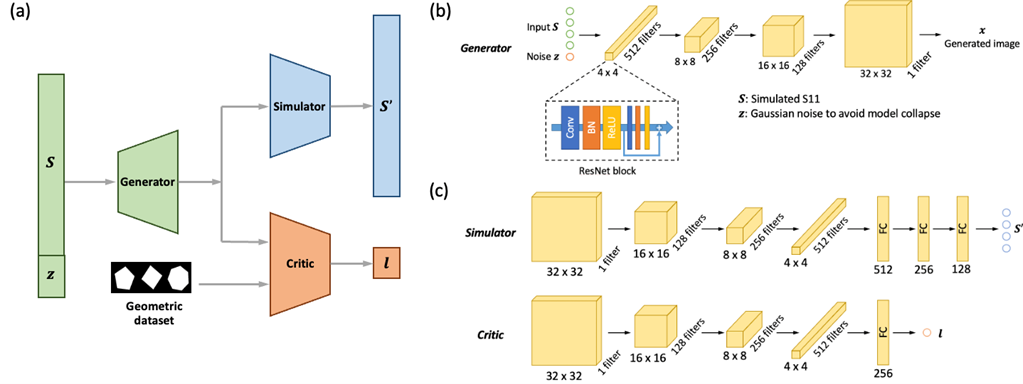
Intelligent Antenna Design using Generative Adversarial Network [paper]
Featured by low conduction loss and high radiation efficiency, dielectric resonator antennas (DRA) have been considered as a promising antenna type for the applications of 5G technologies at 60 GHz band. To date, the design of the DRA mainly depends on the intuitive reasoning and trial-and-error process, which is time-consuming and resource-demanding. To address this challenge, a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based approach is developed to automate the design of DRA structures. The GAN model incorporates a simulator and generator for the DRA modeling and DRA structure design, respectively. A training dataset of the pattern-annotation pairs of geometric shapes and S11 parameter was generated to train the GAN model. During the training process, the distribution of this dataset was captured by the end-to-end GAN model. The trained GAN model is capable of predicting DRA performance as well as generating new DRA structures according to a given S11 spectrum.